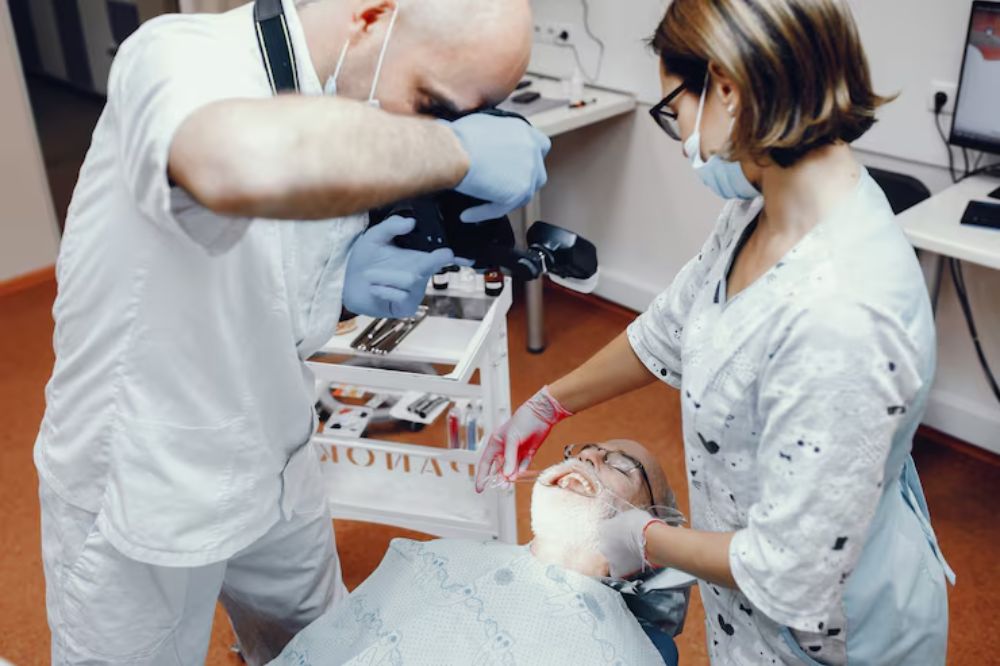
Early detection of oral diseases is crucial to maintaining long-term oral health. Patients searching for an oral surgeon near you often want clarity on why a dental biopsy is performed and how it contributes to proper diagnosis and treatment planning.
What Is a Dental Biopsy Procedure?
A dental biopsy procedure involves removing a small piece of tissue from your mouth to examine it with the help of a microscope.
This helps determine if any abnormal tissue is benign, precancerous, or malignant.
Biopsies are often recommended when unusual growths, sores, or discolourations appear in the mouth.
The process is invasive in nature and is performed using anesthesia, which helps you recover faster.
Why Oral Disease Diagnosis Matters
Accurate oral disease diagnosis is essential to prevent oral conditions from worsening. A biopsy provides definitive information about the type of tissue involved and guides the next steps in treatment.
Early identification of disease ensures better outcomes, reduces risks, and can prevent the spread of serious conditions like oral cancer.
How Pathology in Gibsonton Supports Oral Health
A specialized pathologist in Gibsonton work alongside oral surgeons to analyze biopsy samples. Laboratory testing helps detect subtle changes in tissue that may not be visible during a regular dental examination.
Pathology ensures that the treatment plan addresses the root cause rather than just the symptoms.
The Role of an Oral Surgeon
An oral surgeon in Gibsonton plays a vital role in performing biopsies. They begin the process by evaluating the affected area to choose the right biopsy technique to help achieve patient comfort throughout the treatment.
Oral surgeons also collaborate with pathologists to interpret results and plan any follow-up treatment.
Common Types of Dental Biopsies
There are different biopsy methods, and the best one to choose depends on the size and the location of the tissue. An oral surgeon will help you choose the best option from the below listed ones:
- Excisional biopsy – removal of the entire lesion for small growths
- Incisional biopsy – removal of a portion of a larger lesion
- Brush biopsy – a less invasive technique for superficial tissue
Your oral surgeon will determine the best method for accurate diagnosis and minimal discomfort.
How Patients Should Prepare
Before the procedure, your oral surgeon may recommend that you
- To avoid eating food and drinks for a few hours
- Inform your dentist about the medicines you take or about your health condition
- Following oral hygiene instructions
After the biopsy, it’s important to follow care instructions to reduce infection risk and promote healing.
Monitoring Results and Next Steps
After the biopsy, the tissue sample is sent to a lab for analysis. Once results are available:
- Your oral surgeon will review the findings
- Discuss whether further treatment is necessary
- Create a customized plan to manage or remove abnormal tissue
This approach helps you achieve timely and effective intervention.
Protect Your Smile with Timely Biopsies
Dental biopsies are an important part of maintaining your oral health. They help you catch issues early and support accurate treatment planning. If you’re looking for Pathology in Gibsonton, our team at Orange Blossom Oral Surgery provides expert evaluation, attentive care, and professional biopsy procedures. We offer a personalized approach to help keep your smile healthy and strong. Book an appointment with our team today.
FAQs
Is a dental biopsy painful?
Local anesthesia is used, so most patients feel minimal discomfort.
How long does it take to get biopsy results?
Typically, results are available within a few days to a week.
Can a biopsy detect oral cancer early?
Yes, biopsies are crucial for early detection of potentially malignant tissue.
Are there risks involved with a dental biopsy?
Minor swelling or bleeding may occur, but serious complications are rare.